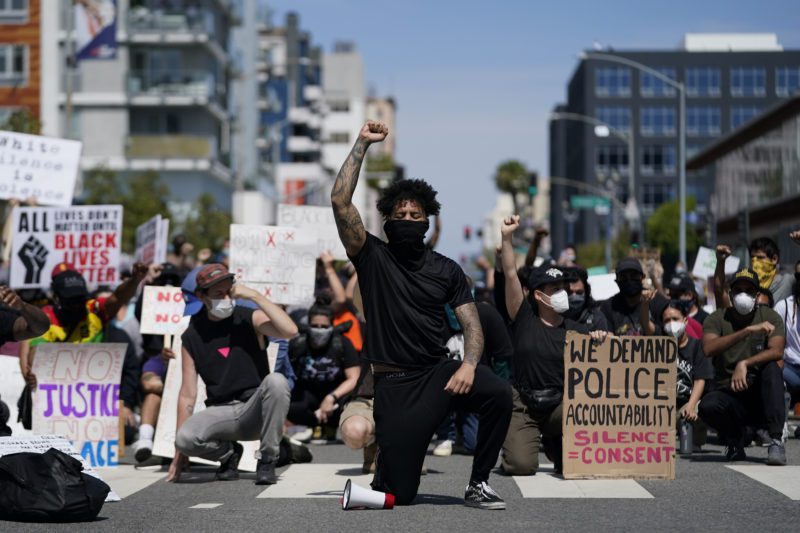
DETROIT (AP) — Proposed federal legislation that would radically transform the nation’s criminal justice system through such changes as eliminating agencies like the Drug Enforcement Administration and the use of surveillance technology is set to be unveiled Tuesday by the Movement for Black Lives.
Dubbed the BREATHE Act, the legislation is the culmination of a project led by the policy table of the Movement for Black Lives, a coalition of more than 150 organizations. It comes at an unprecedented moment of national reckoning around police brutality and systemic racism that has spurred global protests and cries for change after several high-profile killings of Black Americans, including George Floyd.
“We stand on the shoulders of giants and there has been 400 years of work that Black people have done to try to get us closer to freedom,” Black Lives Matter co-founder Patrisse Cullors said.
“This moment is a watershed moment. I think this moment calls for structural change and transformative change in ways that we haven’t seen in a very long time. We see this opportunity to push for the BREATHE Act as a part of what we’re calling the modern-day civil rights act.”
The legislation was first shared with The Associated Press, and is scheduled to be revealed in a Tuesday press conference that is slated to include an appearance by singer John Legend.
The proposed changes are sweeping and likely to receive robust pushback from lawmakers who perceive the legislation as too radical.
University of Michigan professor and criminal justice expert Heather Ann Thompson acknowledged the uphill battle, but noted that that the legislation is being introduced at a highly opportune time.
“I think those programs that they’re suggesting eliminating only look radical if we really ignore the fact that there has been tremendous pressure to meaningfully reform this criminal justice system,” said Thompson, author of “Blood in the Water: The Attica Prison Uprising of 1971 and Its Legacy.” “Every radical piece of legislation that we’ve ever passed in this country, it has passed on the heels of the kinds of grassroots protests that we saw on the streets. The will of the people indicates that if they just keep putting a Band-Aid on it, these protests are not going to go away.”
No members of Congress have yet said they plan to introduce the bill, but it has won early support among some of the more progressive lawmakers, including Ayanna Pressley and Rashida Tlaib, who also are due to participate in the news conference.
The bill is broken into four sections, the first of which specifically would divest federal resources from incarceration and policing. It is largely aimed at federal reforms because Congress can more easily regulate federal institutions and policy, as opposed to state institutions or private prison facilities.
The other sections lay out a detailed plan to achieve an equitable future, calling for sweeping changes that would eliminate federal programs and agencies “used to finance and expand” the U.S. criminal-legal system.
The elimination would target agencies such as the Immigration and Customs Enforcement, which has come under fire in recent years for its aggressive deportation efforts, and lesser-known programs such as Department of Defense 1033, which allows local law enforcement agencies to obtain excess military equipment.
The act, which also seeks to reduce the Department of Defense budget, would institute changes to the policing, pretrial detention, sentencing and prosecution practices that Cullors said have long disproportionately criminalized Black and brown communities, LGBTQIA people, Indigenous people, and individuals with disabilities.
It would establish the Neighborhood Demilitarization Program, which would collect and destroy all equipment like military-grade armored vehicles and weapons in the hands of local, state, and federal law enforcement agencies by 2022.
Federal law enforcement also would be unable to use facial-recognition technology, which many communities across the nation already have banned, along with drones and forms of electronic surveillance such as ankle-monitoring.
The bill would end life sentences, abolish all mandatory minimum sentencing laws and create a “time bound plan” to close all federal prisons and immigration detention centers.
Recent polling from the Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research shows a dramatic shift has occurred in the nation’s opinions on policing and race, with more Americans today than five years ago believing police brutality is a very serious problem that too often goes undisciplined and unequally targets Black Americans. The polling found that the majority of Americans say the criminal justice system needs major changes, including many saying it needs a complete overhaul.
Cullors said she is hopeful the bill will gain support and build upon the change the movement has produced since it first began seven years.
“We are calling for the federal government to be creative in identifying new approaches to dealing with harm and violence in our communities as well as developing investments into building healthy, sustainable and equitable communities,” she said.
The bill would direct Congress to establish a Community Public Safety Office that would conduct research on non-punitive, public safety-focused interventions that would be funded through new grants, and programs like a “Free Them All” Matching Grant Program offering a 50% federal match for projected savings when states and communities close detention facilities, local jails, and state or youth prisons.
According to the document, it also would bring about numerous changes for parents and children, such as removing police, school resource officers and other armed security and metal detectors from schools.
The coalition first began releasing policy recommendations in 2016 and is in the midst of relaunching its Vision for Black Lives 2020, which will be rolled out and expanded over the coming months leading up to a planned National Black Convention in August of 2020.
“We are a generation that wants to make sure that the needs of all Black people are met,” Cullors said. “We believe the BREATHE Act is that legislation. It’s an act that is pushing us to look at the future of this country, an act that is is mandating and demanding a new future and policies that are courageous and visionary.”
___
Kat Stafford is a member of The Associated Press’ Race and Ethnicity team. Follow her on Twitter at https://twitter.com/kat__stafford.